
September 10, 2020
By Zayna Khayat, Future Strategist, SE Health
Aging and Community
The first chapter of our book ‘The Future of Aging’ entitled ‘Aging and Community’ looks at the shifts underway in where and how people physically live, and how they define and create community – physically and virtually. In our research, we uncovered four key shifts underpinning aging and community. Here we take a deeper dive into what the 4 shifts are and how they’ve changed in a post-pandemic context.
The Four Key Shifts in the Future of Aging & Community
Pictured below are the shifts we identified in Chapter 1, and to the right, is our appraisal of how they’ve changed because of the pandemic. Following a ‘traffic-light’ approach, green means progress was accelerated, yellow means progress was slowed compared to pre-COVID speed, and red means progress stopped, reversed or the pre-pandemic baseline got catastrophically worse. Overall, the pace of change that we described in this theme/chapter of our book is slowed down somewhat due to the pandemic. Here is how each of the 4 shifts play out:
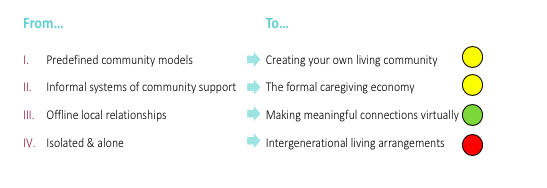
How Things Changed
Because this lens of aging (community & housing) is so directly linked to physical space, it’s no surprise that spatial distancing ended up also meaning social distancing, shattering nearly every element of community for aging adults.
There’s No Place Like Home
Pandemic or not, the underpinning desire of older adults to neither seek out nor accept pre-ordained models for where and how to live has not been altered. If anything, home has been re-positioned as the only place (and safest place) anyone should be right now, and this focus will remain for at least another 18-24 months. This sentiment is reflected in analyst estimates that people will seek out even more (and more creative) ways to stay in the home & community of their choice for as long as possible.
Social Isolation Worsens
Despite home and community becoming the most important way to limit infection and heal if you did get sick, due to Draconian spatial distancing policies enacted globally, levels of social isolation of the aged have exploded. This phenomenon has especially had devastating consequences in congregate, multi-resident settings where family caregivers of the elderly were somehow downgraded from their role as essential partners and caregivers, to “family visitors”, with highly restrictive visitation policies. Many experts anticipate the separation of older adults from their families, friends and support networks will lead to a secondary pandemic from the fallout of decompensated physical health, new and exacerbated mental health challenges, and accelerated dementia and cognitive decline. There are already numerous anecdotal stories, and published evidence that this has transpired.
Family Caregivers Become #MoreThanAVisitor
One good thing that might come out of how we went backwards on social isolation and balance of power to families is how activated the family caregiver community has become, globally. This community galvanized at a scale we have never seen before, with aggressive political advocacy, storytelling in traditional media channels, large-scale social media movements (#MoreThanAVisitor) and healthy doses of anarchy and rebellion. Muscle memory for positioning the family caregiver as an essential partner in the life and care of their loved ones is in place, and will serve well in keeping momentum towards the shifts in this chapter as we settle on the next normal for society in the coming months.
How Things Got Better
Countering the reverse progress on community and socialization, are three positives that would not have transpired had the pandemic not happened.
Digital Connection Thrives
A larger proportion of aging adults are experimenting with socially connecting to family, friends, volunteers and service providers via digital channels. In many cases, new services emerged to help aging adults, access digital tools such as free or heavily discounted access to wifi, tablets and smart phones (telcos, tech giants, senior living operators, many banks) and free digital literacy training programs. For example, Best Buy and Google Nest joined forces to leverage seniors-trained Geek Squad agents to install Google Hubs in senior living buildings so residents can have a simple, immersive experience engaging with their loved ones. My sense is that the shift towards more meaningful virtual connections has accelerated such that the pre-COVID baseline of digitally un-connected seniors will never return.
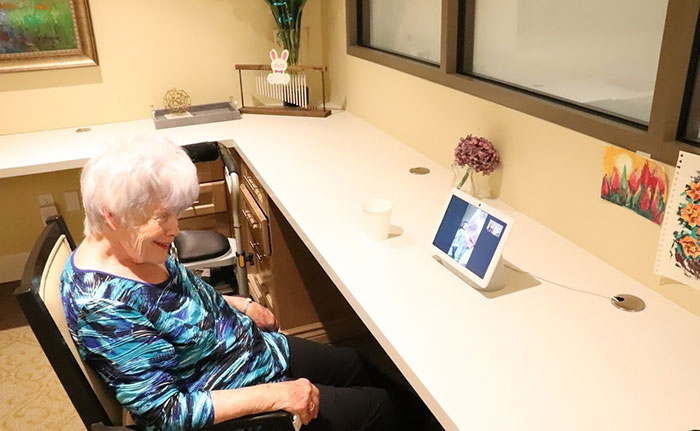

Caption: Best Buy and Google Nest help seniors stay connected Source
A New Vision for Long Term Care Living
The disproportionate percent of COVID deaths that occurred in nursing homes (from 40% of all deaths in most countries, to as high as >80% in places like Canada), will have years of adverse impact on occupancy rates in multi-unit congregate living facilities for seniors. Not only will demand drop, operators of these facilities face new regulations that restrict occupancy levels. This will pave the way for new, creative intergenerational and other living arrangements in one’s own community to emerge, as was already detected in the early signals covered in this chapter of the book.
The Caregiving Economy
The shift to a formal caregiving economy got a massive boost through the pandemic, as new Uber-like services emerged overnight, matching seniors who need groceries, transportation, food, medicine, or companionship, to an army of people with a lot of spare time, goods, expertise and passion to step up and help. Interestingly, many of the social innovations that emerged got online and into the field in a matter of days; whereas pre-pandemic these pop-ups and startups would have taken months or years to get the operating model and business model sorted out. One exciting example of rapid social innovation was the Friendly Neighbour Hotline launched by the social innovators at OpenLab in Toronto. It is a phone number seniors in need could call to organize deliveries of essential supplies. In 10 days they launched the hotline, and within a few days after that > 750 citizens volunteered to be shoppers and drivers.

Looking ahead: Adjusting Your Pathway Towards the Future of Aging
The Future of Aging book provides an evidence-based, comprehensive roadmap to guide anyone who has a stake in policies, products or services for an aging society. We’ve highlighted above how the terrain for the future of the community, socializing, informal caregiving, housing and living has been altered by the global COVID-19 pandemic. There have been some roadblocks, a few detours, and some entirely new laneways have opened up. But the journey remains the same. The call to action now for citizens and innovators in this space is to be aware of how the shifts have changed, so you can adjust – and in some cases pivot – your work now so you can ‘future-proof’ for tomorrow. Our aging population depends on you, and it can be a powerful way to honour the disproportionate loss and suffering of older populations and their families through this crisis.